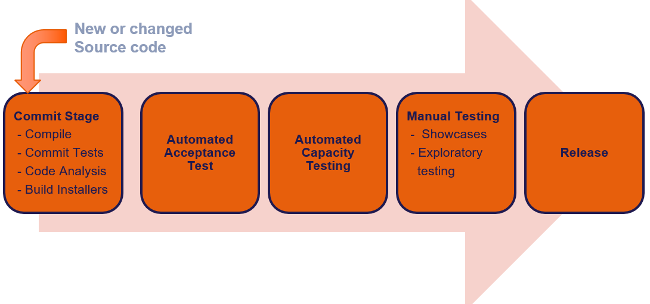
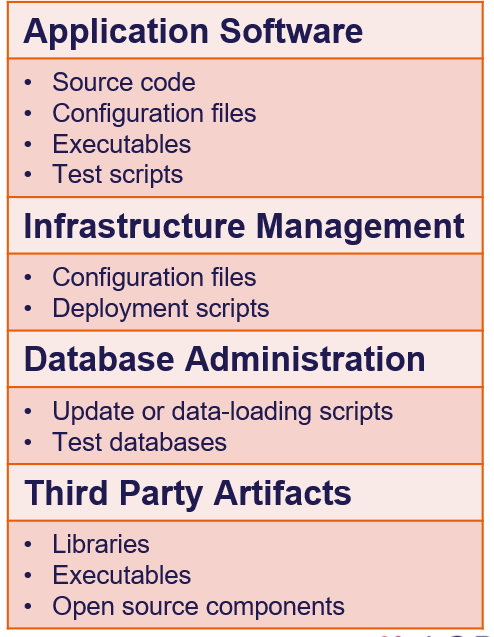
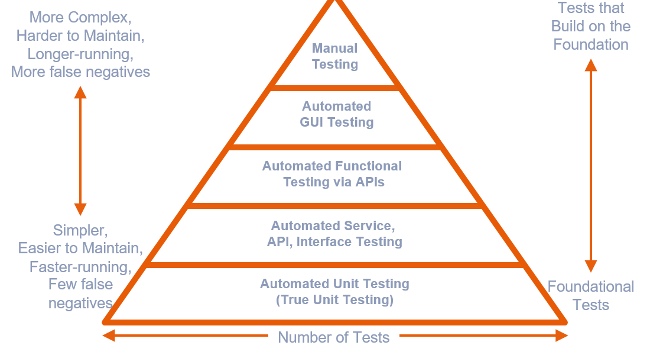
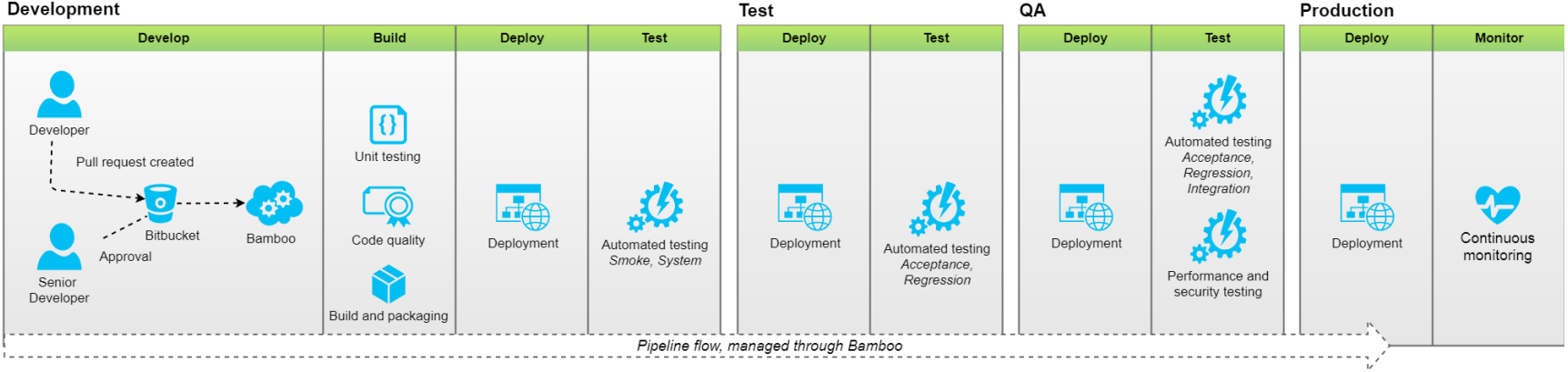
- Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early.
- Continuous Integration doesn’t get rid of bugs, but it does make them dramatically easier to find and remove.
- Developers check out code from the repository to work on it locally. Ideally, they create a new branch for the feature they want to implement.
- When their feature branch is ready, they run tests locally in their development environments.
- Once all tests pass, they push the commits to the single source repository.
- Whenever there are changes on the repository, a CI server checks out the changes and performs a “build and test.” A build and test is when the CI server builds the entire system on the developer’s feature branch and runs all the unit and integration tests.
- The CI server notifies the team of the integration result. There should generally be four outcomes: failed build, successful build, failed tests, successful tests.
- If there’s a failure, the team fixes the issue ASAP.
- When the feature branch is merged to the main branch, they repeat steps 2–6.
- They continue to develop and repeat the steps 2–6 whenever there’s new code to be checked in to the repository.
- Check in code in frequently.
- Automate the build and test portion.
- Always test the code locally before checking it in.
- Never merge any failed branches to the main branch.
- Return its status back to successful if you’re the developer who causes the failed build or test.
- Make it your top priority to do so once the fail happens
- Continuous Deployment is closely related to Continuous Integration and refers to the release into production of software that passes the automated tests.
- In a typical software development setup you expect multiple developers to be developing in their own feature branches which they periodically integrate to a common development branch.
- When a piece of code is integrated (or even before it’s integrated) , it is essential that a verification step is available that can quickly ensure that the particular integration would not break existing functionality, would not degrade performance or even would not introduce security loopholes.
- In-order to achieve speed, it is essential that verification is automated. i.e. this should be comprised of series of automated tests that would cover most critical aspects of the software and could be executed in a reasonable period of time.
- The development team has a big role to play in ensuring the continuity of the pipeline. For example what happens when a build fails or test fails?. Fixing such issues should take top priority or otherwise it will diminish the returns of the CI/CD process.
- not mandatory but if the deployment is based on containers, it will reduce the complexity.
-
Jenkins in master-slave mode as the build server
-
Jenkins Pipelines to drive the CI process
-
Git Hooks to trigger builds with code commits
-
SonarQube as the code quality tool
-
Robot Framework for automating functional tests
-
JMeter for performance testing
-
OWASP ZAP for security scanning
-
With Jenkins
- you'll only need to enable Pipelines and define your workflows to be able to run tests and deployments on your branches.
- Step 1: Start with a default pipelines to be run on feature branches
- Step 2: Add a new pipeline for the master branch
- Step 3: Protect your release branches
- Step 4: Use pull request to promote changes to production